Microsoft introduced a disturbing chatbot of their own recently, Bing, which occasionally argues with users and threatens them.
Google responded to Open AI's Microsoft-backed generative AI tool ChatGPT this week with a demo of an AI chatbot of their own, but after the chatbot called Bard made a factual error during the Google AI demo the company's stock lost $100 billion. You read that right. And Microsoft hasn't fared much better, introducing its Bing AI search chatbot only to discover that it occasionally argues with and threatens users.
AI may be the hottest technology startups can leverage to build their own tools, and professionals and students alike can use to search for information in a new way that moves beyond Google's traditional search algorithms. But pretty much everyone agrees the early-stage AI chatbots have some problems and need significant improvements. Bard is still in beta, but it raises questions about Google's ability to ensure a continuation of its reputation for reliable search data.
Is Generative AI Reliable?
What's the problem? The natural language learning model that new chatbots are trained on helps them to connect patterns in data input into their systems and generate language-based answers. But this means they might not spit back facts verbatim. Sometimes they go off script, and there are two problems with that in particular:
- AI chatbots generate essay-format answers for the user, but they don't cite sources or verify that facts are reliable. This means if a student uses AI to write a term paper, it could be half nonsense even if it sounds good. AI has been found to repeat conspiracy theories and misinformation, while also being prone to misunderstand or misinterpret information out of context when attempting to draw connections between facts. In the case of Google's Bard demo, the chatbot stated a fact that was wrong: that the James Webb telescope was the first to take a picture of a planet outside our solar system. The first was actually the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope, in 2004. Training could fix this, but only if companies training AI and the public or professional teams giving the AI feedback have reliable facts themselves or can vet their own bias. And AI could easily take this type of fact and apply it to the wrong circumstances. AI needs to understand nuance of meaning, not just context and pattern recognition.
- AI can offer information from multiple sources quickly, but without knowing where it came from, it's easy for the end user, the human, to misunderstand or misinterpret facts as well because the context is lost on where the AI found that information.
How To Make The Most of Generative AI ChatBots
Could ChatGPT make coding faster for engineers? We'll skip the hysteria you're probably already sick of in the news: yes, ChatGPT will probably replace some jobs. No, it can't write a decent college paper for you yet, any more than the current Dalle can draw hands, though this is the first iteration of a tool that will get much more sophisticated with time and input. Especially since everyone is training it by using it and giving feedback.
What we want to know is, how can a generative AI tool be used to do busywork paired with the intelligence of a software developer? How can an AI chatbot help a startup founder write a business plan? How can AI help you save time doing research while helping you verify the validity of its answers?
Some programmers recently discovered the ChatGPT generative AI tool can program a website. This raises the possibility of using the ChatGPT to do the mundane coding with engineers to tweak the code and do the overall design and direct architecture. It may make tech workers nervous in a time of tech layoffs to know that their jobs and coding skills might not be completely future-proof, but it has always been true that new technology makes work more efficient but still needs someone in charge to tell it what to do. AI is far from sentient, and it won't be in charge of the tech industry any time soon. The AI is the robot janitor, the AWS cloud services leveraged by engineers. People are the architects or the CEO, and what they do with AI determines not only their own usefulness but what the AI evolves into. The AI is our data turned into a pattern recognition program. The AI is us. But not that smart. It certainly need direction.
OpenAI's ChatGPT is so popular the site often crashes when the tool is at capacity due to overwhelming demand and public curiosity.
Ways To Get The Most Out of Generative AI Tools
What can ChatGPT do to replace basic coding? Here are some people playing with ChatGPT for everything from building websites to scraping them and explaining code. Check out how other engineers and tech entrepreneurs are playing with this tool.
Watch ChatGPT build a website from scratch.
Use a loophole to scrape a website with ChatGPT.
Automate data science tasks with ChatGPT.
Use ChatGPT to build a business idea and a website.
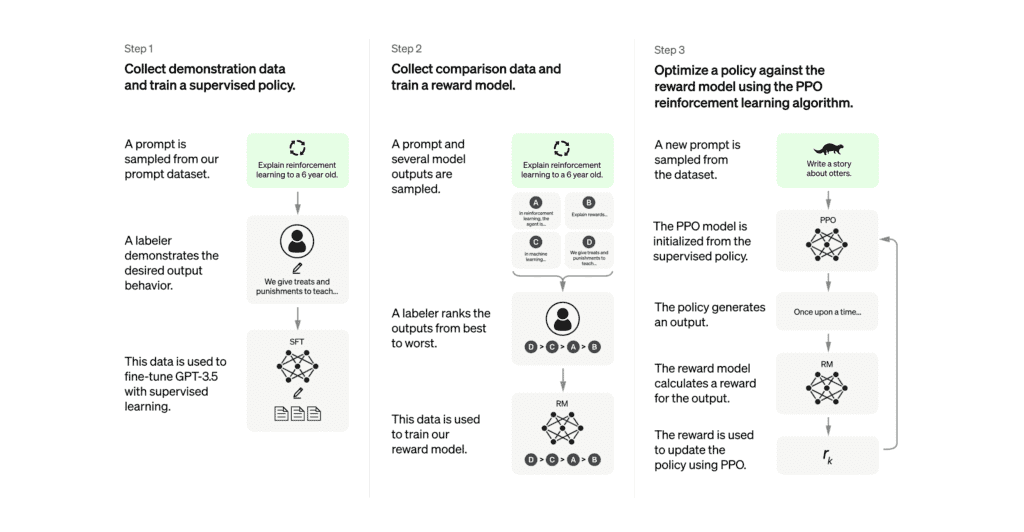
How ChatGPT is trained. Image courtesy OpenAI.
Tips For Using ChatGPT
What we've noticed so far in the infancy of ChatGPT is this:
ChatGPT isn't good for writing your entire essay or building your entire website yet (at least not until someone builds a tool on top of the AI to use it that way, which is surely already in the works), but what it can do well is give you an outline and useful ideas to inspire your own work.
Here are some tips to use ChatGPT to code or write or create a business idea or website effectively, while you do the hard work:
- Try using ChatGPT to get unstuck when coding. Ask for ideas. Ask for more details. Ask for explanations and more resources you might not find on your own.
- Whatever you're asking for -- an essay outline, a list of priorities for a business plan -- you can request that ChatGPT put the answer in an outline format in "bullet points only." This changes the result from a vague question-dodging essay answer to data you can pull ideas from or facts you can fact-check.
- Then ask ChatGPT to fill out that outline with more details. Want a business plan? The tool can track your previous question to a limited extent, so you can ask for context or more detail and fill in the gaps.
- Ask ChatGPT for the latest business idea for XYZ type business. The tool pulls from many sources it won't identify, but it can research ideas more quickly than you can and can do the busy work for you. Then you add what's missing. If you're asking for information about business building you might normally glean through networking or mentorship, you can use ChatGPT to be a sort of mentor for your startup in this way, pulling from sources of information you otherwise can't get to or don't know are out there.
A sample of how ChatGPT handles a request to debug code.
What Happens for Google?
Google has more than egg on its face. The company seems to be responding to public calls for the next revolution in search: AI instead of organic search algorithms.
But Google already does this. Several years ago, Google could only pull web results on text searches that were mostly nouns. Then the company started using AI to allow users to type in questions in the search bar in full sentences. The results that appear above organic search results attempt to answer the question by finding that answer on various websites or aggregating data into a text answer with a link to the source.
Google may be panicked that its entire business model is at risk from generative AI and it needs to catch up, but keep two things in mind:
- Every chatbot makes mistakes, and AI is in its infancy. Amazing tools are in the works, and next-gen AI will change the game in every industry over time. The fact that Google's AI made a mistake in a demo at least suggests it was a live demo.
- Google already DOES generative AI, and the way the search is set up allows users to find the source of the data. We think that a combination approach between the way ChatGPT tries to generate original text using input data and Google's citing sources could be the future of this particular use case for generative AI. Time will tell how many other things it can do that we haven't even thought of yet.
Before you ask, this article was written by a human. The human makes no claims as to the fitness of this information for any given intent or purpose, but she is (slightly) smarter than a generative AI bot and hopes you can tell the difference between human-generated logical thought, however flawed, and the dodgy avoidance and ephemeral musings of AI. For now.